![]()
By Aanchal Vasandani, Sr. Vice President – Content at VIBGYOR Group of Schools, Mumbai
Many children grow up hearing, “Don’t cry” or “Be strong” when they’re hurting. While these words are often meant to comfort, they unintentionally send a message: that emotions are something to suppress or ignore. Few children are given the space to truly sit with their feelings, name them, and understand them. Instead, they learn to brush things off and move on, without ever learning how to process them.
Imagine a child being told, “Your feelings are valid, let’s explore them together.”
This is what emotional intelligence fosters: the ability to notice feelings, make sense of them, and respond with thoughtfulness. It is not about being calm all the time; it is about growing up with the tools to navigate life’s highs and lows with awareness and empathy.
When we nurture emotional intelligence early, we don’t just shape better behaviour; we raise children who are emotionally grounded, resilient, compassionate, and capable leaders.
Here’s why emotional intelligence, taught early, becomes a lifelong source of strength and well-being:
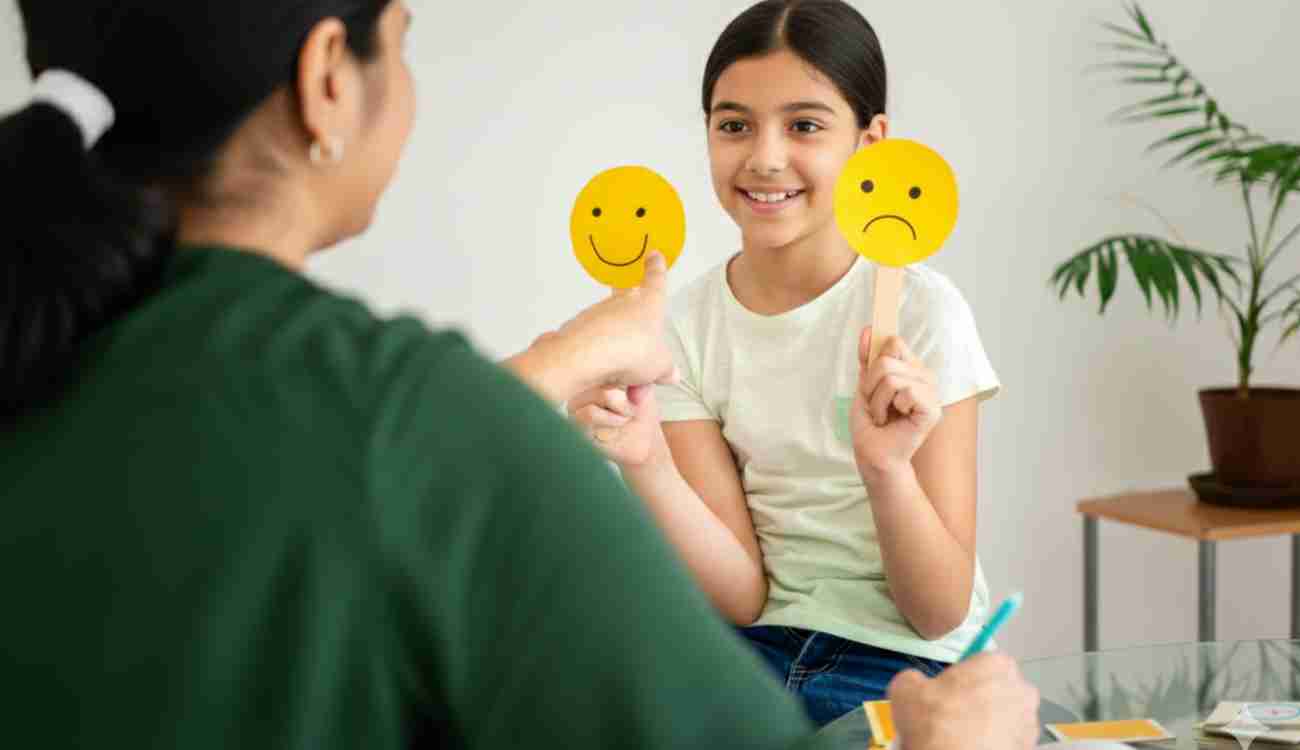
Children learn to name what they feel
For many adults, saying “I feel overwhelmed” or “I’m scared” still feels unfamiliar. For a child still learning about the world, identifying and naming emotions can be especially challenging. Early emotional education provides children with the vocabulary to express their inner feelings and experiences. Instead of lashing out, they can say, “I’m angry.” Instead of shutting down, they can say, “I’m sad.” The ability to name emotions is the first step in processing them and in learning that every feeling is valid.
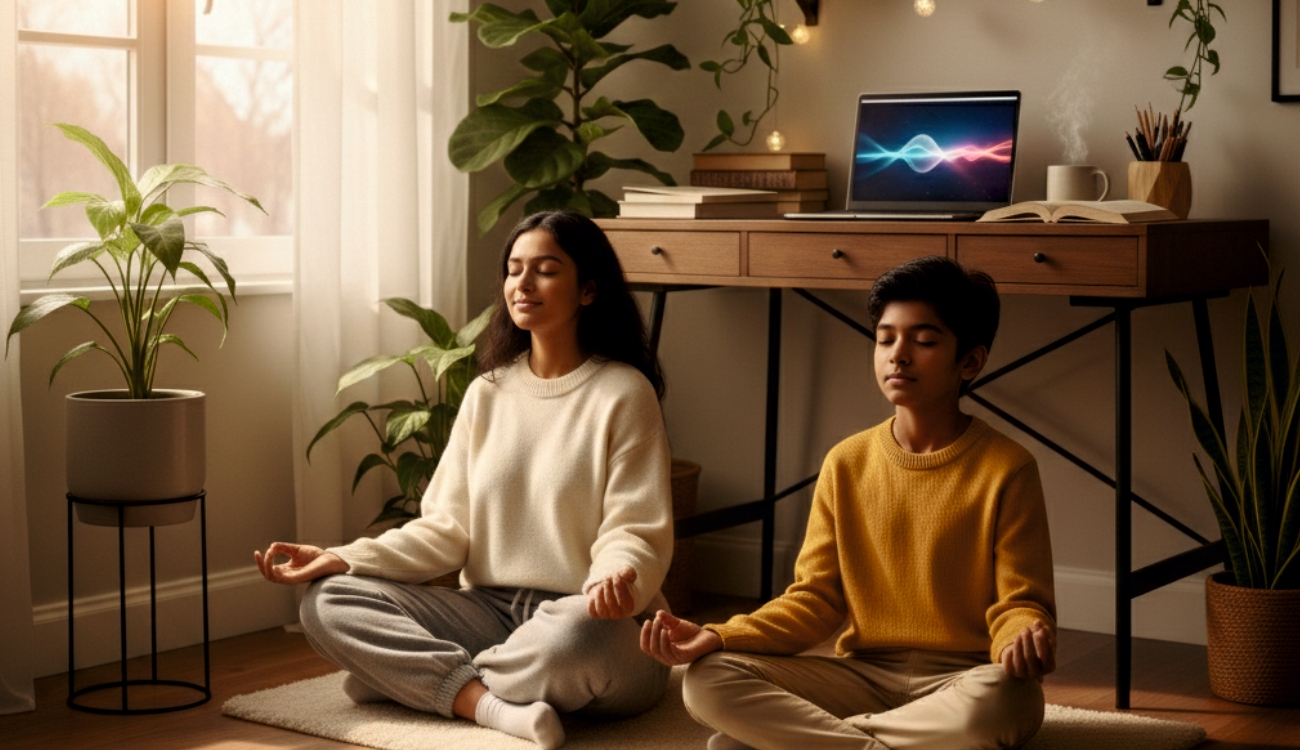
They learn to manage emotions before meltdowns happen
Self-regulation is about recognising emotional signals and responding before things spiral, not just about bottling up feelings. When emotional intelligence is taught early, children begin to notice their own cues: a racing heart, clenched fists, or the urge to cry. With consistent support, they learn grounding techniques, calming routines, and the power of a deep breath. Over time, these habits grow into lifelong emotional resilience.
Empathy becomes second nature
Empathy doesn’t develop in a single moment. It’s nurtured through small, daily interactions such as comforting a friend, noticing someone is upset, or understanding the impact of one’s actions. Teaching emotional intelligence early helps children connect beyond themselves. They begin to value shared experiences and learn to respond with care. These early seeds of empathy grow into compassionate adulthood, supporting strong friendships, teamwork, and caring communities.
It builds confidence rooted in self-awareness
Confidence is not just about being outgoing or assertive. Genuine confidence comes from understanding one’s own strengths, boundaries, emotions, and needs. Children who develop emotional intelligence gain this awareness early. They become better equipped to handle setbacks, voice their needs, and stand their ground without aggression. This kind of confidence is steady because it’s grounded in self-understanding, not external validation.
Relationships become healthier and more meaningful
Children who can express their emotions clearly and listen with empathy build stronger connections with parents, peers, and teachers. Friendships become more authentic. Conflicts are approached with curiosity rather than fear. And as they grow, these skills enrich relationships at home, in school, and eventually in workplaces and personal lives. Challenges don’t disappear, but emotionally intelligent individuals are better prepared to navigate them.
Emotional intelligence becomes a lifelong anchor
Life brings uncertainty, disappointment, and change. Emotional intelligence offers a steady anchor through it all. Children who learn to tune into their emotions are more likely to seek help when needed, offer support when possible, and embrace vulnerability as a form of strength, not weakness. These qualities don’t just help them survive tough times; they enrich the joyful ones too.
In Summary
Every day offers us a chance to model emotional intelligence, whether as a parent, teacher, caregiver, or mentor. A gentle check-in like, “What are you feeling today?”, a steady presence in a tense moment, or honestly sharing one’s own emotions can all become powerful lessons in themselves.
Teaching emotional intelligence is not about perfection. It’s about presence. When children feel seen and heard, they grow into adults who can see and hear others, and themselves, with greater clarity and compassion. That’s how we raise not only happier, healthier individuals, but also thoughtful, empathetic leaders who make the world a better place.
Source: Brainfeed